COVID 19 Vaccine Pipeline
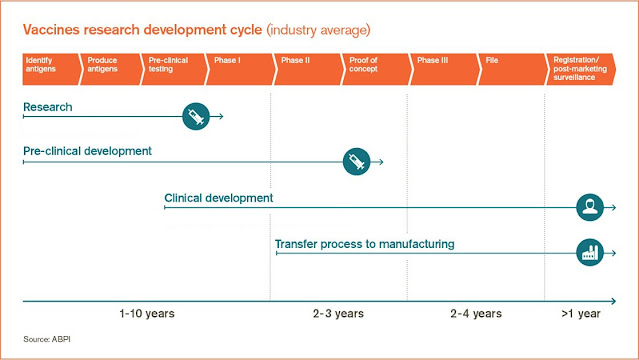 |
| Figure 1: Vaccine development timeline. Source |
Candidate Vaccine | Developer | Design | Evaluation Phase |
PiCoVacc | Sinovac | Inactivated SARS CoV 2 CN2 strain with alum | Phase 3 |
ChAdOx1-S | University of Oxford & AstraZeneca | Adenovirus-vectored vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, encoding the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 | Phase 3 |
AD5 Vectored COVID19 Vaccine | CanSino Biological Inc. & Beijing Institute of Biotechnology | E1/partially E3-deleted, replication-defective human adenovirus 5 (Ad5) vector (Ad5-N-V) expressing the SARS-CoV N protein | Phase 2 |
LNP encapsulated vaccine | Moderna & National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases | mRNA-1273 lipid nanoparticle encapsulated mRNA-based vaccine that encodes for a full-length, prefusion stabilized spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 | Phase 2 |
INO-4800 | Inovio Pharmaceuticals & International Vaccine Institute | Plasmid pGX9501, encoding for the full length of the Spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 is administered through electroporation (Celectra device) | Phase 2 |
AG0301-COVID19 | Osaka University AnGes Takara Bio | DNA vaccine encoding antigens from SARS-CoV-2 | Phase 2 |
ZyCov-D Vaccine | Cadila Health Care Ltd | DNA vaccine encoding antigens from SARS-CoV-2 | Phase 1 / 2 |
Inactivated Vaccine | Wuhan Institute of Biological Products & Sinopharm | Inactivated SARS CoV 2 strain | Phase 1 / 2 |
Covaxin | Bharat Biotech | Inactivated Whole-Virion | Phase 1 / 2 |
NVX CoV2373 | Novavax | Full length recombinant SARS CoV-2 glycoprotein nanoparticle vaccine adjuvanted with Matrix M | Phase 1 / 2 |
BNT162b1 and BNT162b2 | BioNTech/Fosun Pharma/Pfizer | Nucleoside modified RNAs are formulated in lipid nanoparticles. BNT162b1 encodes a SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) antigen, while BNT162b2 encodes the virus’ full-length spike protein antigen. | Phase 1 / 2 |
GX-19 | Genexine | DNA vaccine expressing SARS-CoV-2 S-protein antigen. | Phase 1 / 2 |
Inactivated Vaccine | Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (IMBCAMS) & Yunnan Center for Disease Control and Prevention. | Inactivated SARS CoV 2 | Phase 2 |
Gam-COVID-Vac Lyo. | Gamaleya Institute | Adenoviral-based vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 | Phase 2 |
Protein subunit vaccine | Clover Biopharmaceuticals, GSK and Dynavax Technologies | S-Trimer protein that resembles the coronavirus spike protein | Phase 1 |
Protein Subunit vaccine | Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences & Zhifei Longcom | Chinese Hamster Ovary cells producing a modified form of the coronavirus spike protein Adjuvanted recombinant protein (RBD-Dimer). | Phase 1 |
Covax19 | Vaxine Pty & MedyTox | Spike protein along with an adjuvant called Advax | Phase 1 |
Protein Subunit | University of Queensland, GSK and Dynavax Technologies | Molecular clamp” technology containing stabilized Spike protein
| Phase 1 |
COVAC1 | Imperial College London | LNP containig a self-amplifying ribonucleic acid (saRNA) vaccine | Phase 1 |
CVnCoV | Curevac | mRNA encoding the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 packaged into lipid nanoparticles. | Phase 1 |
ARCoV | People's Liberation Army (PLA) Academy of Military Sciences, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences and Walvax Biotechnology | SARS CoV 2 mRNA Vaccine | Phase 1 |
VLP vaccine | Medicago Inc, GSK and Dynavax | Plant derived virus like particles | Phase 1 |
2. Yarmarkovich et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Epitopes Predicted to Induce Long-Term Population-Scale Immunity. Link



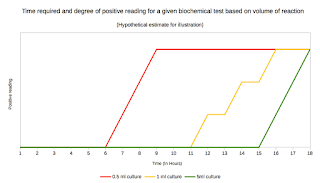
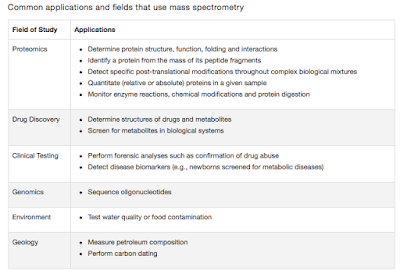
Comments
Post a Comment